Software development lifecycle may sound scary or confusing, but in fact, it’s a simple method of delivering software applications. Planning to start a software development project? Then this guide is here to map out your journey towards a successful, working app!
In this article, we’ll explain the term “software development lifecycle” and go through its usual stages. We’ll also cover different software development life cycle models so you can get a full overview of the topic.
What Is Software Development Lifecycle?
Software development lifecycle, otherwise known as SDLC for short, is a term used by software houses to name a methodology of delivering high-quality, working software that meets the client’s requirements, deadlines, and budget. Coined in the 1950s and the 1960s, it has become a valuable tool used for thousands of applications for different industries and purposes (follow Techopedia if you want to learn more about the history of SDLC). Currently, its precise standards are covered within the ISO/IEC 12207 international norm defining the tasks required to develop software and maintain it.
A standard development cycle is divided into a couple of phases (more on that below) that define the type of tasks to get done inside them. Each task inside a project life cycle is then assigned and measured upon completion to ensure high-quality software.
Still confused? Think of the software development lifecycle as a roadmap with clear guidelines that take you all the way through the process of software engineering, from planning to maintenance. It’s also there to improve the efficiency of the development team and achieve the ultimate goal of meeting the client’s needs while staying within the budget and deadline.
What Are The Stages of Software Development Lifecycle?
The software development process is usually divided into six to eight steps. Why does that number vary? Depending on the project’s scope and deadline, some project managers may combine steps or omit them altogether. However, this act doesn’t (or shouldn’t) influence the overall quality of the product in any way, so if you hear that your development team wants to do six phases instead of seven, don’t freak out.
Depending on the SDLC model you use, these stages may be repeated as needed. An iterative model (described later in this article), for example, works in sprint-based iterations that go back and forth between the phases multiple times to deliver better results.
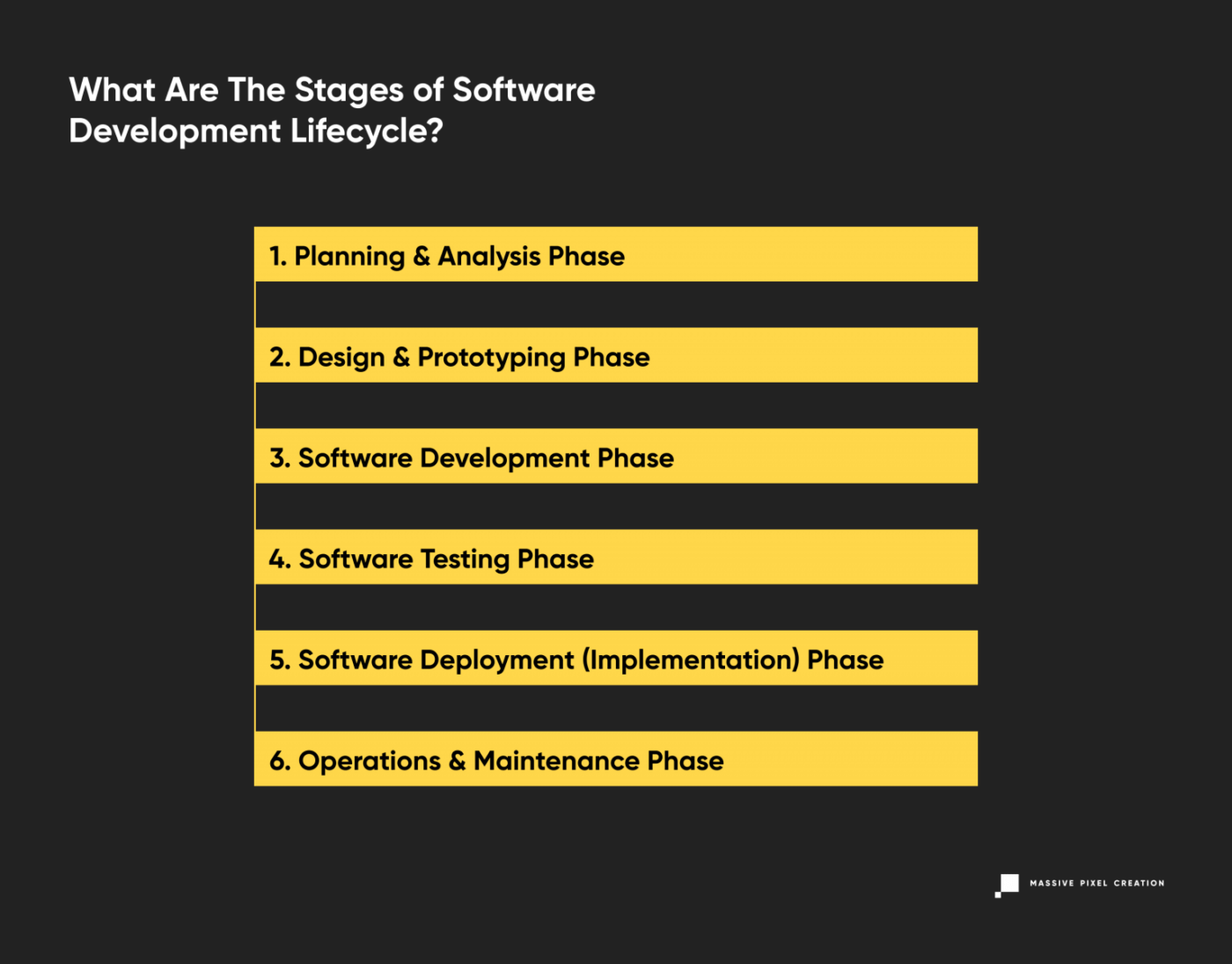
Let’s review the traditional distinct work phases of the entire SDLC process.
1. Planning & Analysis Phase
Careful planning and requirement analysis are crucial in delivering great software. At this stage, the customer works together with the software house team to create a detailed scope of the project and calculate the time and resources needed.
A mutual understanding of the product’s features, benchmarks, and goals can be achieved in a number of ways, including workshops, market surveys, expert consultations, stakeholders’ feedback, and more. At this moment, other guidelines are planned as well, such as quality assurance requirements, risk identification, technical scope, production environment, and others.
The result? The team gets a first insight into their future work, while the customer has a clear view of the product’s scope and expected outcomes. Most models use this stage as a starting point and later adjust the tasks to current needs. Agile methodologies have mastered this process, dividing the development time into short increments that involve a specific scope of work established right before the start.
2. Design & Prototyping Phase
The design phase involves much more than just product designers’ jobs. In software development, it’s equally important to create the visual aspect of the end product (the ‘traditional’ perception of design) and the overall system architecture behind it.
Based on the requirements gathered in the previous stage, the software house team now works on designing the product’s structure, including the communication between the elements, data flow, and optional third-party modules. The architecture is created strictly in line with the software requirement specification as well as the deadline and budget constraints determined earlier.
At the same time, the product design team works on wireframes that act as a reference point for the development team and the client. Some SDLC methodologies use rapid prototyping to achieve optimal results that can later be iterated (more on this later). Wireframes and prototypes help the development teams meet customer expectations and move through development faster. They’re a great way of getting early feedback and delivering an MVP version of the future product. Later on, the MVP may be shaped and changed according to new requirements and details.
3. Software Development Phase
Most likely the longest part of the SDLC process, the software development stage requires the most involvement from the development teams and results in a working product including all the pre-agreed features.
The actual development is performed according to the software requirement specification and the wireframes & guidelines established in the design phase. If it wasn’t done at the requirement analysis phase, the entire development process starts with translating the outcomes of both previous stages into an initial set of assignments. Then, the project manager assigns due dates and work schedules for transparency. As the development proceeds, these assignments may change, as the product is delivered according to current business goals or user feedback.
The team rarely uses just one programming language. Most often, it’s a group of software engineers with various skills and experience (a cross-functional team) using a number of programming tools dedicated for delivering specific results. This approach helps to produce high-quality software that meets all business requirements. On top of that, software houses have a set of their own guidelines, standards, and tools to create software. The development team is also supported by tech leaders, project managers, and other roles that help with any bumps in the road.
4. Software Testing Phase
The code is released into a testing environment. The quality assurance team takes over to look for bugs, omissions, and other red flags inside the software. Once again, they check all features against the customer’s expectations and verify the software requirement specification.
Bugs and defects are a normal part of each development process, so you shouldn’t be alarmed by their presence. The software testing phase is designed to provide the highest possible quality in all fields: that’s why the team takes many different user scenarios under consideration and meticulously checks for all options possible. During this SDLC process, the code will probably go back and forth between the developers and QAs until it’s pixel-perfect, stable, and in line with the business requirements. If it’s meant to be combined with third-party software products, the quality assurance team will check for that as well.

The process of software testing involves all sorts of different tests, both automated and manual, like penetration tests, end-to-end tests, validation tests, and more.
Depending on the chosen SDLC model, the testing phase may occur all at once, after delivering the entire code, or interchangeably, in little increments, as more and more features are added to the software. Agile methodologies will lean towards testing during each sprint or release – more on that below.
5. Software Deployment (Implementation) Phase
It’s time to pop that champagne – the code now meets the pre-agreed software specifications! A completely developed product is ready for release to the market and deployed to the production environment. Larger products will require integrating with pre-existing systems. Developers will take one final look at the implemented system, and may work together with QAs and content writers to produce detailed documentation for it.
This stage also involves arranging an infrastructure that’ll support the new product, establishing the server and hosting provider, and creating a strategy for future deployments with product updates.
6. Operations & Maintenance Phase
The system development process is never finished. With time, unexpected bugs can be detected, upgrades may be needed, and feature enhancements might be in order. As the product is now live, the team may observe performance issues or room for improvement.
It’s wise to monitor and review the network performance, environment’s stability, and the product’s behavior after the release. As the product is moved to the final environment and tested by end-users, it needs to remain stable and fast-running. Taking this step leads to faster problem-solving and issue management in case of any changes or critical issues.
The maintenance phase is crucial to meet the ever-changing business requirements, performance standards, and user expectations. It can involve extra development work or code alterations, as well as QA input.
Other Phases
Like I said at the beginning of this section, it’s impossible to pinpoint exactly one ‘proper’ process of software development life cycle. SDLC is a guide, and depending on the project’s specification, scope, and software organization, the software development company may omit some of the phases, merge, or split them into smaller sections as needed. For example, the analysis phase may be divided into business, technical, and other aspects.
In some SDLC process models, like the Agile method, the phases like development and software testing will concur to ensure rapid application development. In others, like the waterfall model, they’ll happen one after another, linearly.
Software Development Process: The Reality
Still thinking of that roadmap comparison from the section above and wondering how this checks out if there are so many variants? You should know that SDLC is not a plan. It’s a tool that you can adjust to your current needs. A traditional perception of planning is rather stiff and leaves no wiggle room, with steps carefully taken one after the other. Most software development methodologies stay away from that concept, as it can be quite binding and unfruitful.
In the next part of this article, we’ll cover the most popular SDLC models and methodologies and explain the core differences between them.
Software Development Lifecycle Models
The number of methods is nearly infinite when it comes to the models of software development life cycle. SDLC methodology allows for a lot of flexibility, and with new ideas and methods of software development, the struggle with choosing the right provider is real.
In this article, I’ll describe these software application development methods that you’ll most likely stumble across when searching for the company to build your product.
Waterfall Life Cycle Model
Perhaps the earliest of all SDLC models, the waterfall model uses all standard phases of software development, putting an emphasis on the planning stage and detailed documentation. Its traditional perception of product development translates to sequential phases that don’t overlap. You may think of it as a ‘production line’ in a ‘software development factory’, where a part of the product is constructed and then passed on.
This model is easy to understand, plan out, and implement, however, as each phase depends on the execution and delivery of the previous one, the entire project is likely to be overdue.
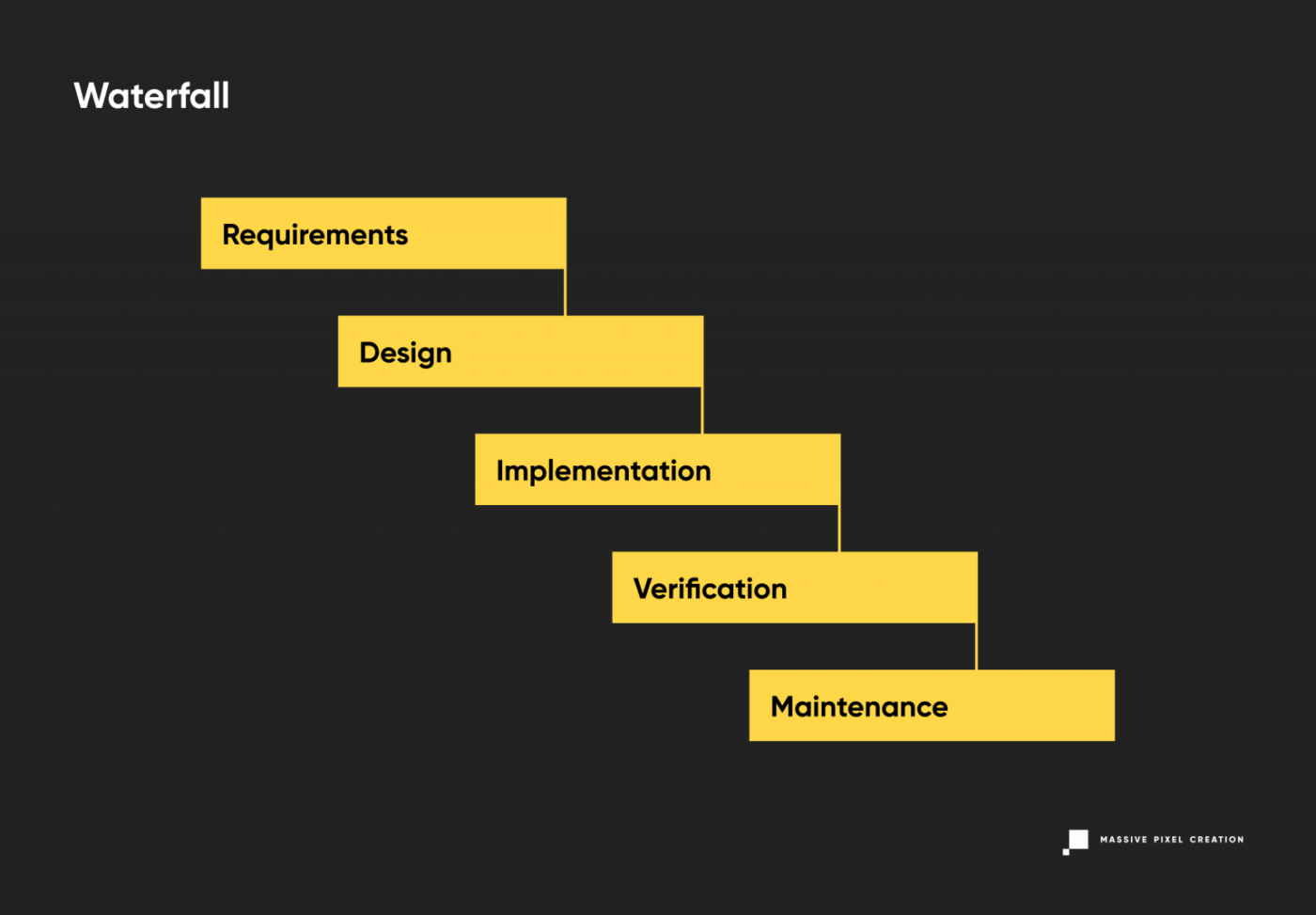
In the waterfall model, the progress flows in one direction and once you put it in motion, there’s a little chance of changing anything as you discover new requirements or constraints to the product. The decision was already made, and the shift will result in missed cost estimates and a ton of work going to waste.
On top of these risks, a significant drawback of the waterfall model is the fact that the end user won’t see a working product, or even a part of it, until very late in the process. This, combined with the high chance of missed deadlines and a long time passing between feasibility analysis and product release (eight to nine months in most scenarios), may result in a software that’s already obsolete when made available to the wide public.
Currently, software houses tend to use modified versions of this methodology, like Sashimi (Waterfall with Overlapping Phases) or Waterfall with Risk Reduction to minimize these uncertainties. Still, these models don’t answer many struggles of modern software development.
Iterative Model
Contrary to the above, there’s not as much emphasis put on preliminary planning in this model of software development life cycle. The SDLC model called Iterative involves breaking a product down into small chunks (iterations) according to the current state of knowledge about the project. All of them go through the standard phases of software development (planning, design phase, software testing, and so on) quickly and are immediately deployed for transparent, tangible results.
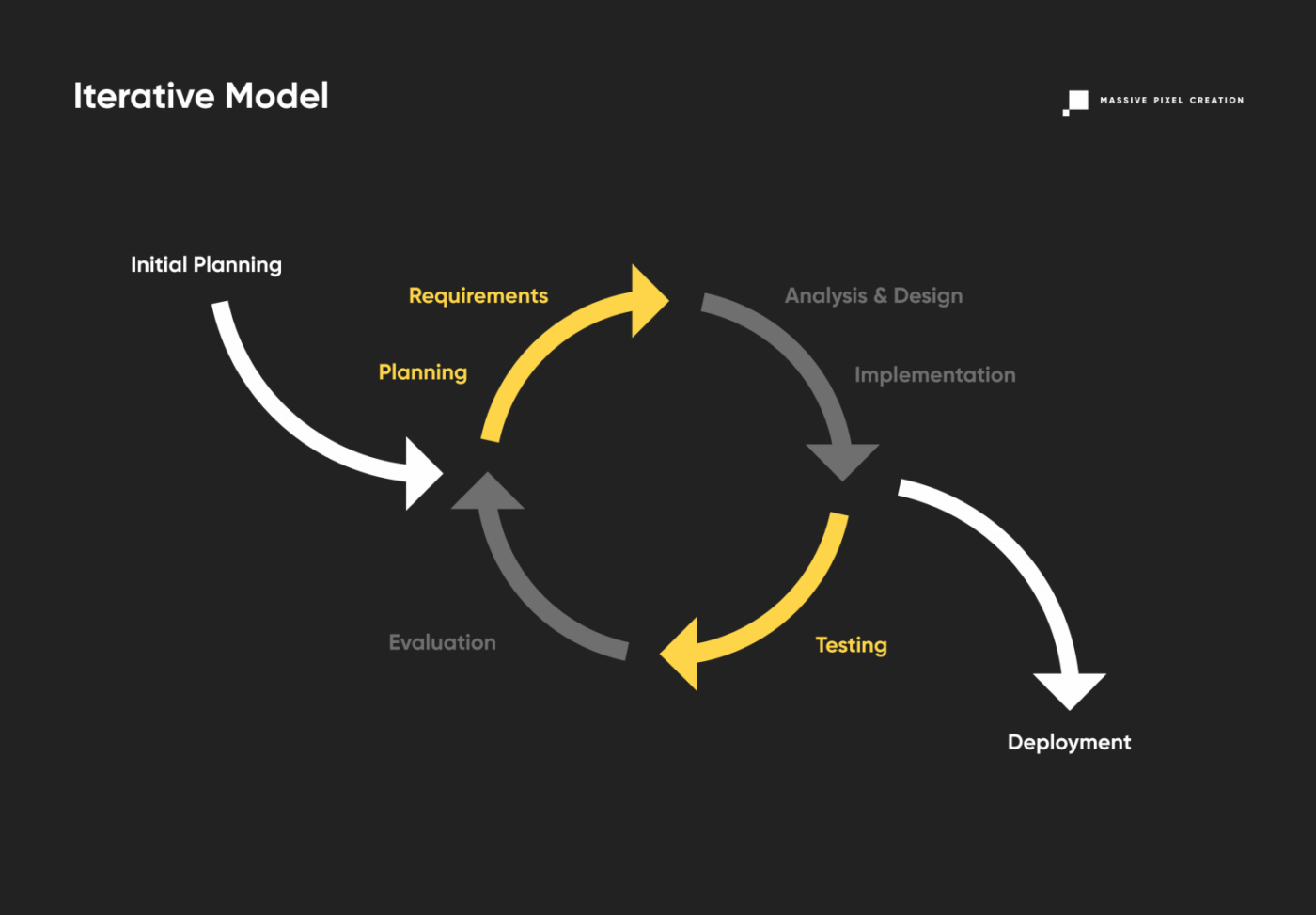
This way, users and clients can pin down the sections that need improvement, and send the product back for the next iteration of development, reducing costs. As the project progresses and more data is discovered, the planning also adjusts to meet new challenges and constraints, working in an iterative manner as well. The iterative SDLC model allows for slight changes to be made during the development, resulting in better market adjustment. Rapid prototyping can enhance client engagement and the feedback process. However, never-ending upgrades to the basic product can eat up resources and lead to out-of-scope software. This can be easily avoided by keeping your roadmap in mind.
Software Prototype Model
Not to be mixed with the iterative model, the software prototype involves fast prototyping of products that don’t have defined requirements. This variant of the software development lifecycle relies heavily on user feedback, as it pretty much construes the scope and details of the project. Therefore, it’s great for high-risk software industry projects with changing business requirements. What’s more, it can lead to huge budget savings, as you invest fewer resources and flaws are easy to locate and fix at an early stage.
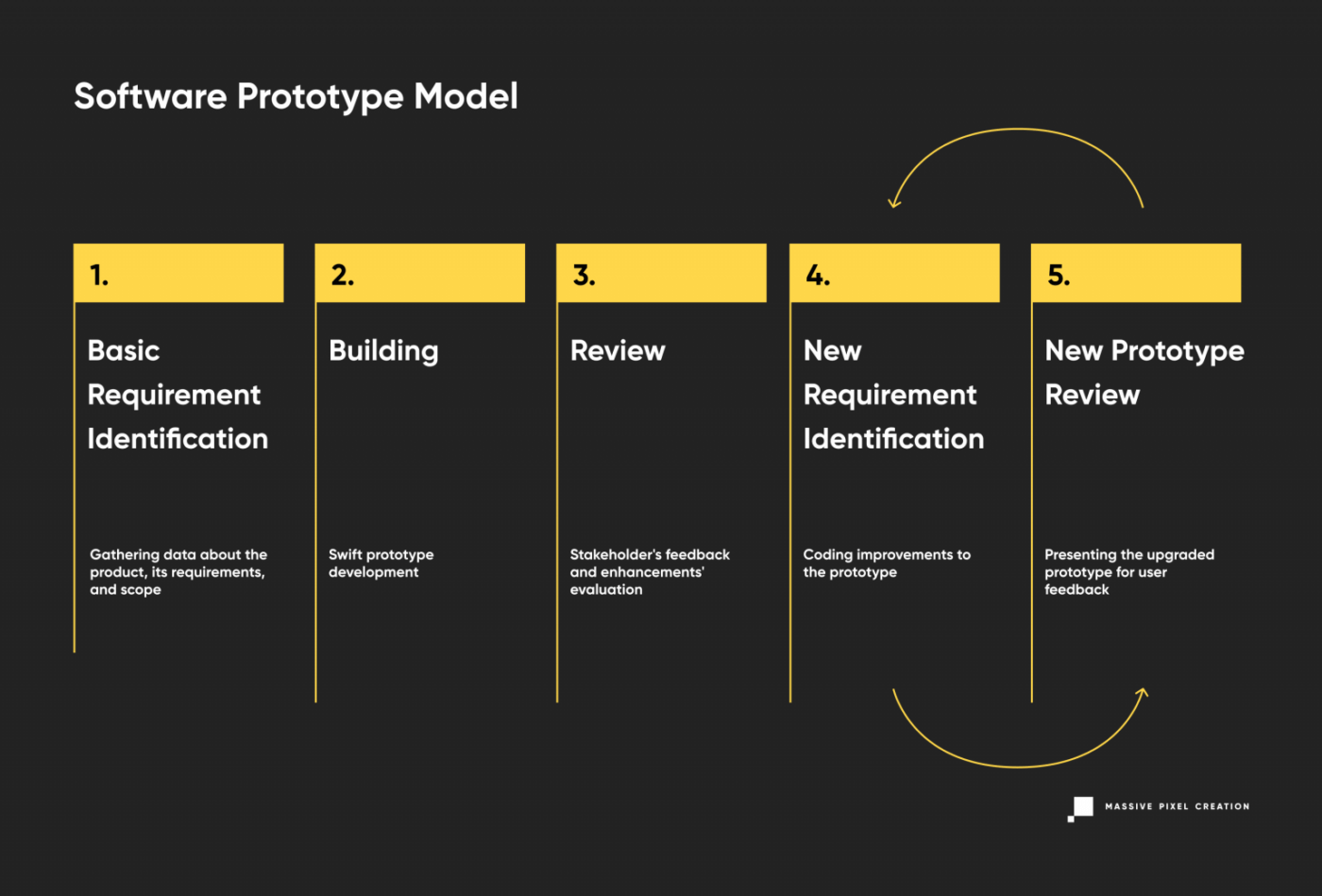
Software Prototype model is often subdivided into three types:
- Rapid prototyping (creating an MVP)
- Evolutionary (adjusting the product according to user feedback)
- Extreme prototyping (developing web applications in stages, starting with a static prototype and then moving on to simulated services and deployment).
However, this approach to software development isn’t risk-free. As the users’ needs can be easily changeable, it may take a long time to complete the ultimate version that pleases the stakeholders.
Spiral Model
The spiral model combines the best features of Waterfall and Prototype models to achieve fast application prototyping and advanced risk analysis. In this case, the team works on preliminary system architecture and design and delivers consecutive prototypes for stakeholders’ evaluation. Once a consensus has been reached, the final prototype is moved to the further stage and through the rest of the development cycles.
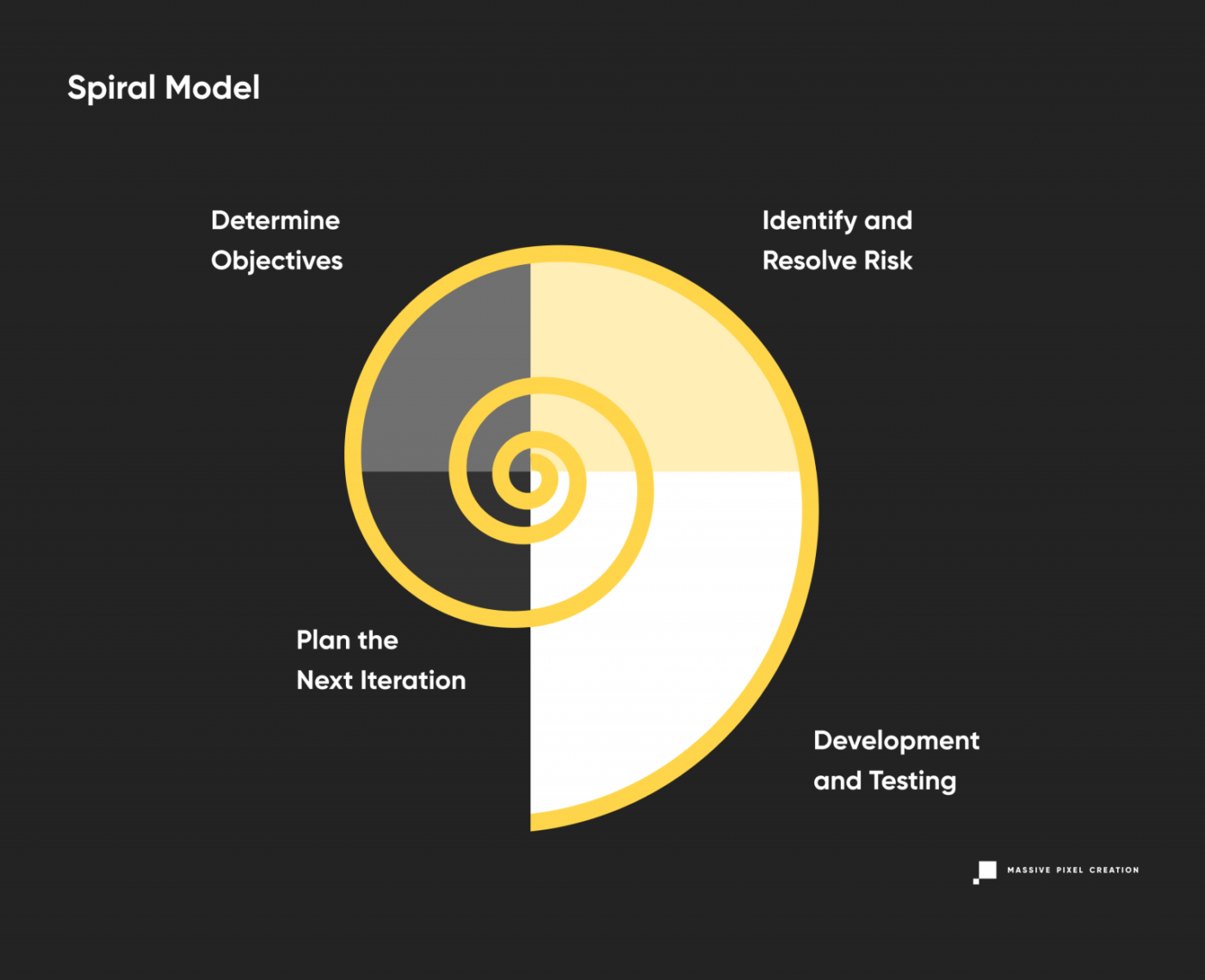
The spiral model enables thorough testing of each step, and even though requirements are set at the beginning, they can easily change with each iteration, reducing the business risk. Extra features may be added as needed, and continuous feedback makes this model more flexible than Waterfall. Still, you need to implement strict procedures to prevent endless spiraling and keep the clear image of the end product in mind.
V-Shaped Model
Yet another variation of the Waterfall model, the V-shaped model follows a parallel structure of tasks while keeping the traditional linear approach to software development. The emphasis is placed on the coextensive verification and validation phase, with coding right in the middle.
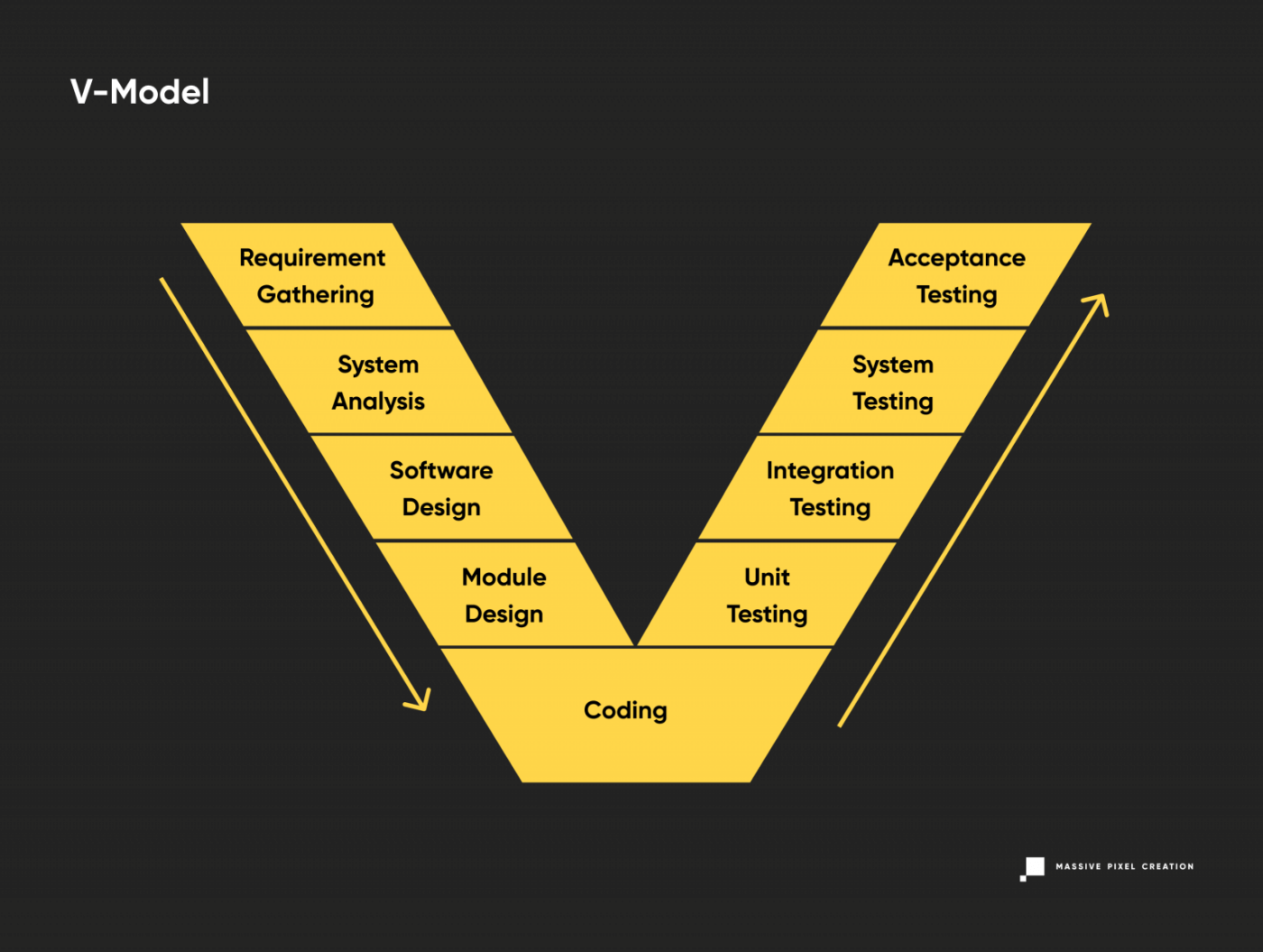
The robust validation phase ensures multi-level testing of all aspects of the newly-developed software. This leads to better risk management, however, its linear, disciplined progress makes it tough to introduce necessary changes at later stages. Also, working software shows up quite late in the cycle, so user feedback is harder to obtain.
This model works well for upgrading existing applications, but may not be so great for new projects that still have more question marks than actual, set-in-stone requirements.
Big Bang Model
The Big Bang Model may sound controversial, as its main characteristic is absolutely no planning. Instead, the team codes and tests as soon as they learn new requirements, which gives them a lot of flexibility, but may also bring unexpected changes and results into the project.
The Big Bang model is good for small projects with short (or unknown) deadlines and tiny teams. It works best when the job needs to be done fast, so every hour spent on planning seems like a waste of time.
As this approach can get quite messy, it’s best to use the Big Bang model with experienced, yet flexible team members (a cross-functional team) who can deliver results quickly and work with little to no input from the stakeholders. It’s also great for academic or practice projects.
Agile Life Cycle Model
The buzzword of modern-era software development, Agile methodologies are great for time-sensitive projects requiring a lot of user feedback. As it’s a disciplined process, many companies introduce roles like Scrum Master to ensure a well-organized, goal-oriented development model.
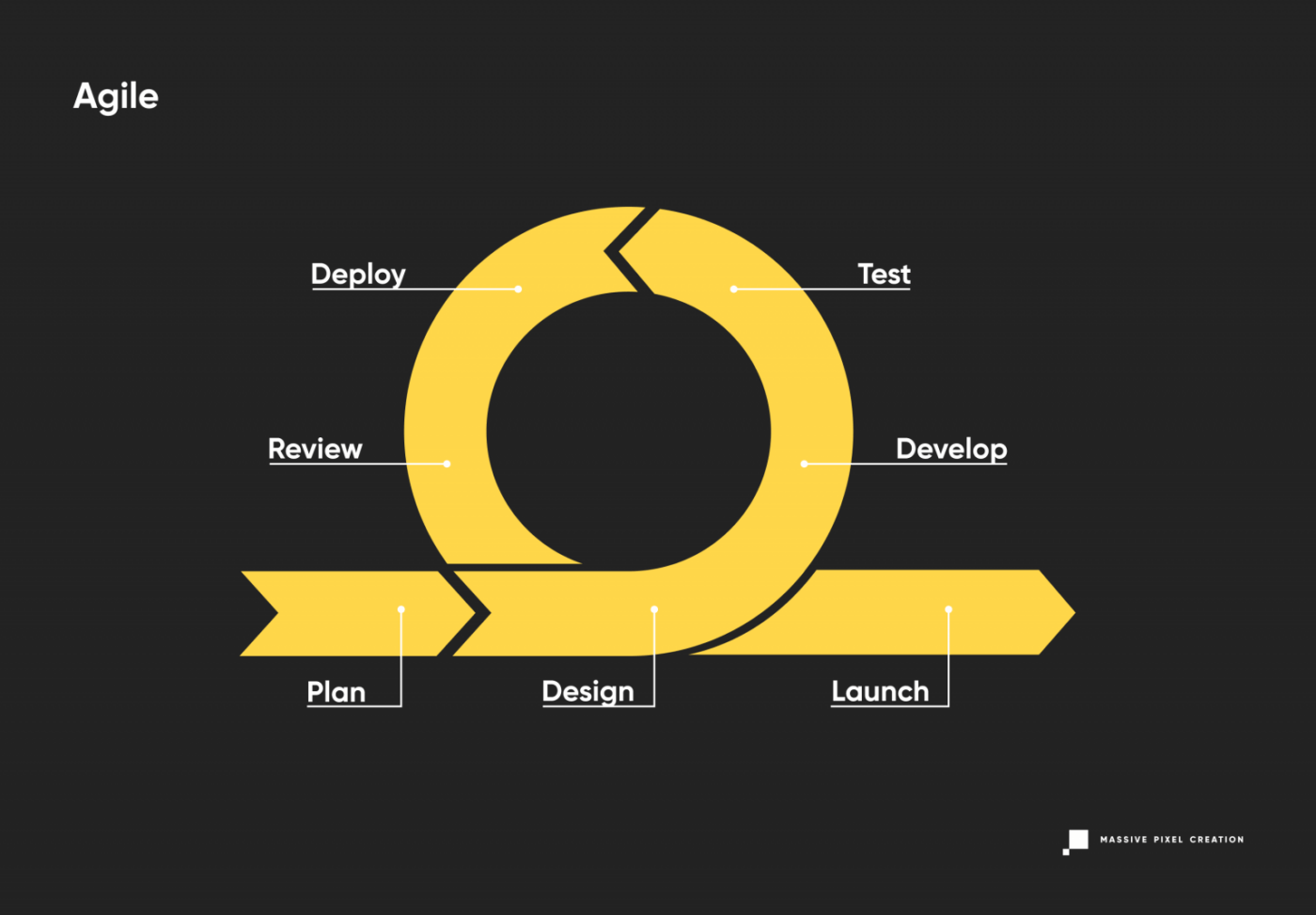
The Agile development model puts the customer first, accepting the inevitability of changes being made mid-project. It combines continuous iterating with robust testing for high quality of the end product and reduced risk; this philosophy divides the project into small sections of work lasting between 1 to 4 weeks.
Usually, if Scrum methodology is also used, each of these periods (called sprints) shares a pattern of kick-off meetings, planning, daily sync, release, and review. This way, the team and the client always have a clear understanding of the upcoming development phase and can adjust the conditions, scope, and process as they go.
The Agile model puts an emphasis on people and interactions between them, caring not only for the result, but also for the dynamics of the team and a clear communication between its members. This is a rare, yet valuable approach that helps to reduce communication gaps, misunderstandings, and time wasted on non-efficient problem reporting. It also ensures constant stakeholder engagement.
Models like XP (Extreme Programming) derive from Agile: XP focuses on the simplicity of development and often mixes the role of a developer and a tester. Another sub-model, Kanban, uses a special visual board to reduce the development time and improve the workflow. This method actually originated in Japanese manufacturing, where visual cues were implemented to prevent inventory pileup.
Other SDLC models
There are many models of software development life cycle. SDLC is a wide concept, and many companies and teams have introduced their own battle-tested methods based on hundreds of software development projects delivered.
Other popular SDLC models are:
- RAD (Rapid Application Development) model, which is similar to the Iterative model, but allows for separate deployment of each iteration;
- Dynamic System Development model, which derives from RAD, but focuses more on user involvement;
- FDD (Feature-Driven Development) model, which is a variant of the Iterative model that bases the project life cycle on features required for the end product;
- DevOps security model, which incorporates the Operations phase into the development loop for instant feedback during the design and implementation stage;
- Lean model, which focuses on easily-changeable software developed efficiently, with less workflow and a smaller budget.
How To Achieve High-Quality Software With SDLC
Regardless of the SDLC model, you choose, introducing some practices to your software development process will help you achieve high-quality results in a timely manner.
Team Communication
Highlighted in the Agile model, this really can’t be overemphasized. Each project will benefit from efficient team communication, as well as the relationship between the team and the customer. Even if you’re not a fan of Scrum or Kanban methodologies, get inspired by the wide pool of soft-skill tools they involve, like daily meetings or retrospective meetings that help solve problems and reduce hold-ups. These have all been battle-tested and bring real value to the project, even if they sound bizarre at first.
Transparency
Make sure that both parties stay on the same page at all times and speak about their expectations during each phase of software development. Let it be simple updates or complicated pivots – this easy rule is a real lifesaver and will cut you loads of extra time spent on fixing bugs and mistakes that weren’t communicated properly.

Continuous Integration
Patching different code snippets at the last minute will almost certainly result in missing deadlines and a lot of stress. Instead, implement continuous deployment and integrate each change into the system as soon as you deliver it to ensure total compatibility and reduce the risk of extra work needed to be done at the last stage.
Version Control
Better safe than sorry! Keep all the code secure and in a single location to prevent any leaks and chaos. Simple security measures such as encrypted Internet connection, logged access, and backup systems can go a long way if something goes wrong. Also, implement a change management system to track individual code input and keep safe, finalized versions of the product separately from unstable ones. Track changes carefully and allow your developers to collaborate on the same codebase.
Fruitful Partnership
Take some time to choose your software development outsourcing company carefully: look through online reviews, testimonials, and portfolios. You can also consider using a video testimonial software to access professional video testimonials – these can provide a more realistic feel for how past clients found their experiences.
Set your own set of expectations towards your partner (including budget and deadlines), and, above all, talk to your candidates!
SDLC: Key Takeaways
SDLC is an excellent way of running, analyzing, and improving the process of developing software. It guides you through all the phases of creating software, from planning to maintenance, and helps you pin down potential problems, hold-ups, and bottlenecks along the way, showing you how to fix them.
The basic SDLC process covers: planning & analysis, design & prototyping, development, testing, deployment, and operations & maintenance.
You can use a variety of models of tested software development life cycle. SDLC models include a traditional Waterfall model and more modern, flexible philosophies such as Agile methodology (with sub-methodologies like Scrum and Kanban that put more structure and detail to the process). Variations like Iterative, Prototype, Spiral, V-Shaped, and Big Bang fall in the middle, as they introduce more space for mid-project changes but are not as adaptable.
Each of these models has a wide portfolio of finished projects. Getting to know them closely will allow you to understand your project’s needs better and make an informed choice.